Synovial fluid provides cushion and lubrication for joints. It will be extracted from the affected joints and examined for markers of infection and inflammation. For example, the total white blood cell (WBC) count will be elevated in the presence of an infection.
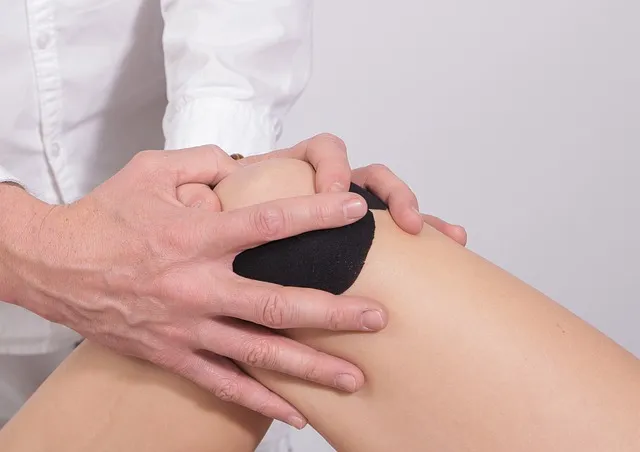
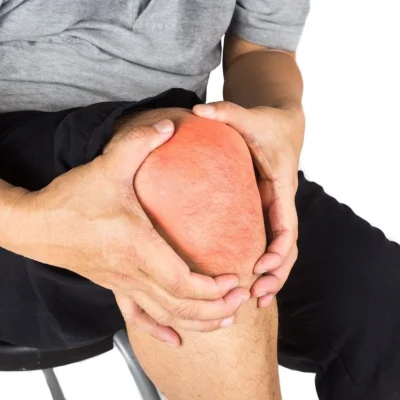
If you are experiencing pain in your knee joint, you are not alone. Knee pain is a common issue that can be caused by a variety of factors, including injury, overuse, arthritis, or other medical conditions. It can significantly impact your quality of life and make simple tasks like walking or climbing stairs difficult.
They’re usually made of stiff plastic or metal with cushions and straps that wrap around your knee and leg. Your provider will tell you which type of brace you’ll need and how often you should wear it. If you experience a direct blow to your knee, such as being hit by a blunt object or falling hard, you could bruise your knee bone.
If you’re age 50 or older, you have a higher risk of getting knee arthritis. Wear and tear on your knees as you age increases the risk of a torn meniscus. A torn meniscus can result from any activity that causes you to forcefully twist or rotate your knee, such as aggressive pivoting or sudden stops and turns. Even kneeling, deep squatting or lifting something heavy can sometimes lead to a torn meniscus. That shows the bones plus signs of soft tissue injury, arthritis, or alignment problems. They may also order an ultrasound or an MRI to help evaluate soft tissue injuries.
Common Causes of Knee Pain
Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press. To find out, they grew neurons in vitro and then doused them with Netrin-4, which sparked the sprouting and branching of CGRP+ (gene-related peptide) pain receptors. It’s the first time that Netrin-4 has been shown to alter the growth of pain-sensitive neurons, Dr. Orange noted. These genes, it turned out, were enriched in pathways that are important for neuron axon growth, the researchers discovered. The keys to sensation, sensory neurons receive and transmit information to the central nervous system. Axons are the tendrils that branch out from them into tissues.
This buildup occurs when there is too much uric acid in your body, a condition known as hyperuricemia. More than 30% of people with gout also have hypertension (high blood pressure). Certain types of arthritis cause acute symptoms, rather than chronic symptoms over time. Here’s a look at some types of acute arthritis that cause your joints to hurt suddenly. Try to maintain a healthy weight and avoid activities that put a lot of stress on your knees. Get treatment if you have symptoms of arthritis of the knee.
The inside of your knee, also called the medial knee or the medial compartment, is the area of the knee that’s closest to your opposite knee. Gout is a common type of inflammatory arthritis that most often starts in your lower limbs, particularly the big toe. It’s caused by a buildup of uric acid in the body, which may then lead to the development of crystals within the affected joints. Unlike arthritis, bursitis tends to have a sudden and severe onset.
Knee pain can be a result of various reasons, some of which include:
- Injury to the ligaments, tendons, or cartilage in the knee
- Arthritis, such as osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis
- Overuse or strain from physical activities
- Obesity, which puts extra pressure on the knees
Managing Knee Pain
It is crucial to address knee pain promptly to prevent further damage and improve your overall well-being. Here are some tips for managing knee pain:
- Rest and elevate your knee to reduce swelling
- Apply ice packs to reduce inflammation and numb the pain
- Use compression bandages or braces for support
- Perform gentle exercises to strengthen the muscles around the knee
Frequently Asked Questions About Knee Pain
Here are some common questions about knee pain:
- Q: When should I see a doctor for knee pain?
- A: If the pain is severe, persistent, or interfering with your daily activities, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional.
- Q: Can knee pain be prevented?
- A: Maintaining a healthy weight, staying active, and avoiding high-impact activities can help prevent knee pain.
Remember, it is essential to listen to your body and seek medical advice if knee pain persists or worsens. Taking proactive steps to manage your knee pain can help you regain mobility and lead a more comfortable life.